LEARN THE HISTORY
AND CONTEMPORARY ACHIEVEMENTS
OF POLISH RESEARCHERS.
TEMPORARY EXHIBITION AT EXPO 2020 IN DUBAI
POLAND THE HEART OF EUROPE
16-23 FEB 2022
The exhibition is organized
on February 16-23, 2022,
at EXPO 2020 in Dubai.
IDEA OF EXHIBITION
The history of medicine on the territory
of present-day Poland dates back much earlier than the Polish statehood.
MORE ABOUT US
Find more about NAWA and our Partners
TEMPORARY EXHIBITION
POLAND THE HEART OF EUROPE
Brain and sensory organs
The brain is the centre of the nervous system and together with the spinal cord forms the central nervous system. The sensory organs are the parts of the nervous system that receive external stimuli, which are then transmitted to the brain. Diseases of the nervous system fall under the umbrella of neurology, with specialisations such as neurosurgery, neuromodulation and neurorehabilitation, among others. Sight disorders are treated in ophthalmology and hearing disorders in otolaryngology and audiology.
Tumours and immunology
Tumours are diseases resulting from the unrestrained division of cells through mutations occurring in them, the loss of repair mechanisms and, consequently, the loss of control by the organism over the natural cell cycle of division and apoptosis (cell death). Cancer is treated by oncology, an interdisciplinary field of medicine that uses various treatment methods, including radiotherapy, chemotherapy and surgery. Haematology is the field of cancerous and non-cancerous diseases of the blood and haematopoietic system. Immunology studies the reactions of the immune system responsible for the body's defense reactions against pathogens or other foreign substances and bodies.
Cardiovascular diseases
Cardiology specialises in diseases of the heart and vessels (the cardiovascular system). It deals with the entire cardiovascular system and cardiovascular diseases, including hypertension, which is diagnosed and treated by hypertensiology. Cardiac surgery is responsible for the surgical treatment of the heart and vascular diseases, while angiology and vascular surgery deal with vascular diseases. The most commonly diagnosed cardiac disorder is coronary heart disease or ischaemic heart disease.
Organ surgery and transplantation, reconstructive and regenerative medicine
Surgery is the branch of medicine involved in surgical treatment. It involves procedures relating to pathologies arising in the course of injuries, dysfunctions and diseases of organs. Due to its broad scope and subject matter, it intertwines with many other fields of medicine, e.g. musculoskeletal surgery is part of orthopaedics and surgery of the nervous system is part of neurology. Plastic (reconstructive and aesthetic) surgery deals with the reconstruction of body defects and the correction of their real or perceived appearance. In organ transplant surgery, known as transplantology, it is not only important to implant a new organ skillfully, but also to prevent its rejection by the recipient's organism, which is closely related to immunology.
Communicable diseases
Communicable diseases are caused by infectious agents: bacteria, viruses, prions or fungi. As a result of their activity, the body's immune strength is compromised. Treatment for infectious diseases is usually causal, aimed at inhibiting pathogenic microorganisms and inactivating toxins of biological origin. Microbiology, especially its branches — bacteriology, mycology and virology — is the study of microorganisms causing these diseases. Vaccination is an effective protection against many infectious diseases; vaccinology deals with research on vaccines.
Paediatric medicine
Paediatric medicine is a separate branch of medicine, which stems from the discovery that a child is not a "small adult". The differences in body structure, physiology and the occurrence of defects and diseases affecting only children and adolescents as well as the different course of many diseases justify its separate management. This is particularly important in paediatric surgery, where anatomical, physiological and metabolic differences are important. Paediatrics deals with paediatric diseases and the care and development of healthy children, whereas diseases of the prenatal and neonatal period fall within the scope of neonatology.
The history of medicine on the territory of present-day Poland dates back much earlier than the Polish statehood. The first skull trepanations were performed as early as several thousand years BC, while the bronze surgical instruments found here are almost 2500 years old.
After the establishment of the Polish state in the 10th century, the driving force behind the development of medicine was first the Church and then the Academy of Kraków, founded in 1364. The Renaissance was a period of particular progress in Polish medical thought, when the works of Polish physicians drew international attention. The flourishing of medical science in the 19th and 20th centuries brought numerous successes to Polish physicians, who contributed immensely to the development of world medicine.
Drawing on centuries of tradition, contemporary Polish medicine is one of the world's leaders and modern institutions conduct pioneering research, contributing to the progress of world medical knowledge.
POLAND THE HEART OF EUROPE
POLAND THE HEART OF EUROPE
TEMPORARY EXHIBITION
MEET OUTSTANDING POLISH RESEARCHERS,
THEIR HISTORY AND ACHIEVEMENTS
HISTORY

Nicoalus Copernicus (1473–1543)
The man who “stopped the Sun, moved the Earth”, creator of the heliocentric system theory, one of the greatest breakthroughs in world astronomy. He was an eminent Renaissance scholar, in his time esteemed more as a physician than an astronomer. A representative of the iatromechanistic school of medicine, he regarded diseases as disorders explainable by the laws of physics and mechanics. He was renowned for his consistent introduction of rational, simple remedies and his promotion of medicine based on close clinical observation and the logic of therapy.

Adolf Beck (1867–1942)
Also studied the physiology of taste, proving that there are different types of nerve endings, separate for each taste, and indicating their location in the structure of the tongue.

Napoleon Cybulski (1854–1919)

Maria Skłodowska-Curie (1867–1934)
Two-time Nobel Prize winner in chemistry and physics, co-founder of the science of radioactivity, discoverer of the elements polonium and radium. She is known as the “mother of radiotherapy” — her research into radioactivity contributed to the development of this field and its use in cancer treatment. She initiated the establishment of the Radium Institute in Paris (1912) and a similar institution in Warsaw, the capital of the reborn Poland (opened in 1932).

Tadeusz Reichstein (1897–1996)
Pioneer of research on adrenocortical hormones, Nobel Prize winner. In 1933 he was the first in the world to synthesize ascorbic acid (vitamin C), which made it possible to virtually eliminate scurvy worldwide. In 1936 he isolated cortisone and later also other adrenal cortex hormones.

Ludwik Teichmann (1823–1895)

Ludwik Hirszfeld (1884–1954)

Tadeusz Tempka (1885–1974)
The creator of Polish haematology. His contribution to world science is mainly in the field of malignant anaemia research. He demonstrated that it was a panmyelopathy and introduced liver preparations and saliva extracts of healthy people (sialotherapy) to treat it.
Jan Prus (1859–1926)
A pioneer of resuscitation. In his research he focused on the possibility of bringing people in clinical death back to life. In 1900 in Lviv, he was the first in the world to successfully apply a direct heart massage in the operating theatre during abdominal surgery.

Gabriel Ochocki (1601–1673)
Physician, doctor of medicine. Author of the treatise Quæstio de motu cordis, in which, parallel to William Harvey in 1628, he described the mechanism of the circulatory system in the human body. These works were revolutionary to previous views on the subject of blood circulation. As he wrote: „Ut sanguinis venosi in cor attractio, ita arteriosa corde transmissio naturalis existit” (both the attraction of venous blood to the heart and the rushing of arterial blood away from the heart occurs naturally).

Zbigniew Religa (1938–2009)

Albert Adamkiewicz (1850–1921)
Author of pioneering studies on the variability of spinal cord vascularisation. The largest root artery of the lumbar spinal cord discovered by him (named the artery of Adamkiewicz) is of great importance in thoracic aorta surgery.

Jan Mikulicz-Radecki (1850–1905)

Ludwik Rydygier (1850–1920)

Franciszek Jawdyński (1851–1896)

Rudolf Weigl (1883–1957)
Developer of a vaccine against typhoid fever (spotted fever). He used lice infected with typhoid fever for his research. He also conducted observations on his own body, when he contracted the disease during his work. The vaccine invented by Weigl was initially introduced in Poland, but soon began to be used throughout the world, helping to significantly reduce the incidence of the disease and prevent epidemics. He was nominated for the Nobel Prize four times, and was given the title of Righteous Among the Nations.

Hilary Koprowski (1916–2013)
Inventor of the first vaccine against polio (poliomyelitis). In 1948, he created a vaccine based on the method of obtaining a live, weakened virus which, however, did not lose its immunogenic properties. Vaccination helped reduce the polio epidemic in Africa and almost eliminated the disease in Poland.

Roman Nitsch (1873–1943)
Author of pioneering studies on rabies and cholera. He demonstrated that the main habitat of rabies bacteria is not the medulla oblongata but the grey matter in the brain. He developed an understanding of the pathways and conditions for the spread of cholera. He was the author of the fundamental monograph „Szczepionki i surowice wraz z nauką o odporności” [Vaccines and Serums Together with the Science of Immunity] (1921).

Tadeusz Browicz (1847–1928)

Odo Bujwid (1857–1942)

Józef Brudziński (1874–1917)

Maciej Leon Jakubowski (1837–1915)
contemporaneity
MEET MODERN RESEARCHERS AND THEIR OUTSTANDING ACHIEVEMENTS
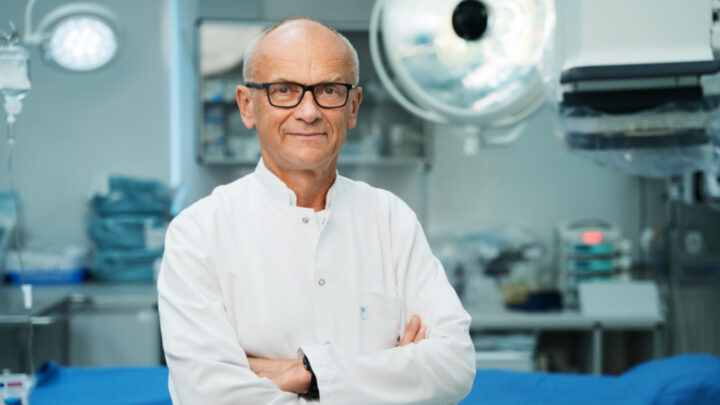
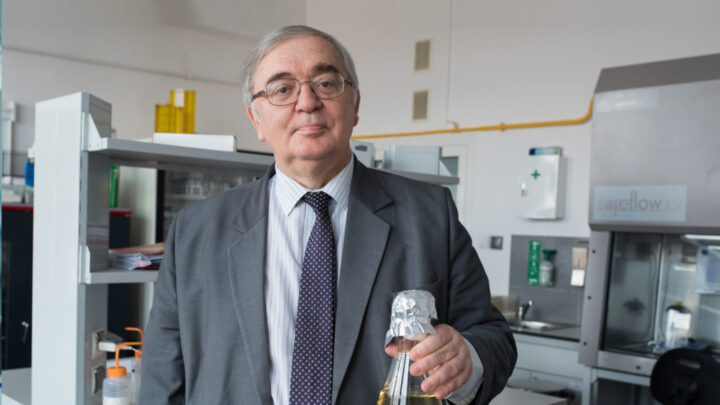
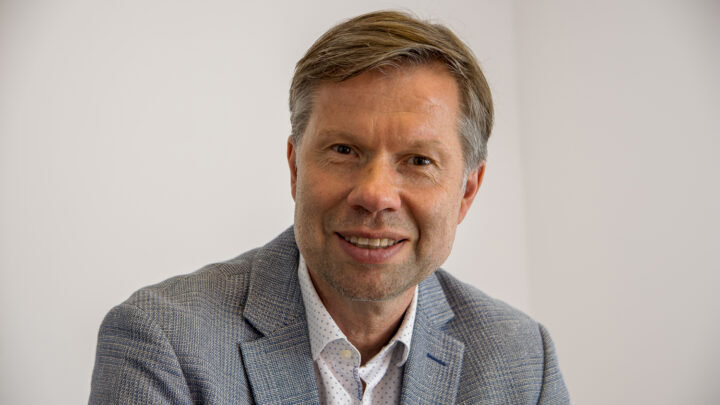
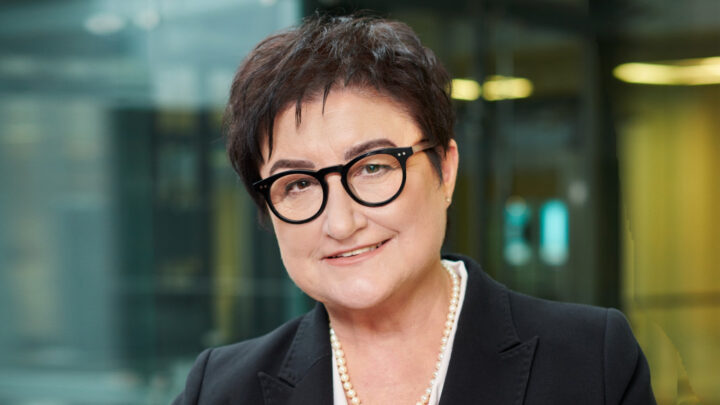
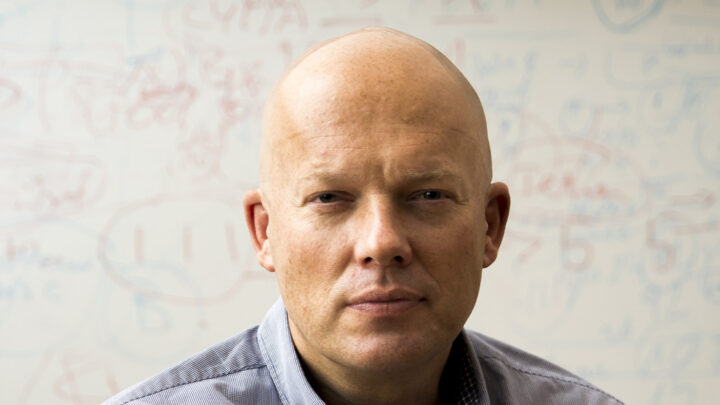
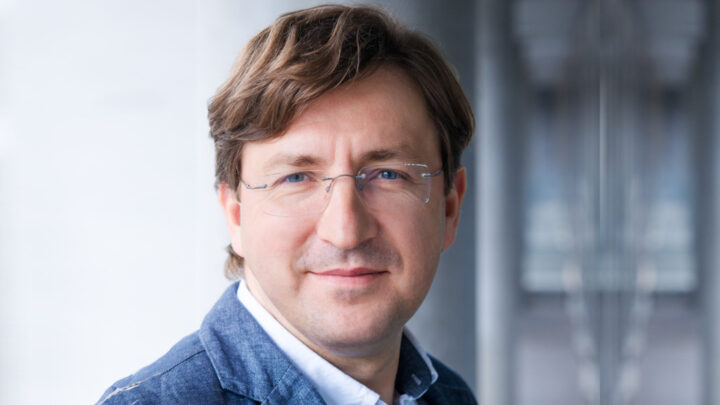
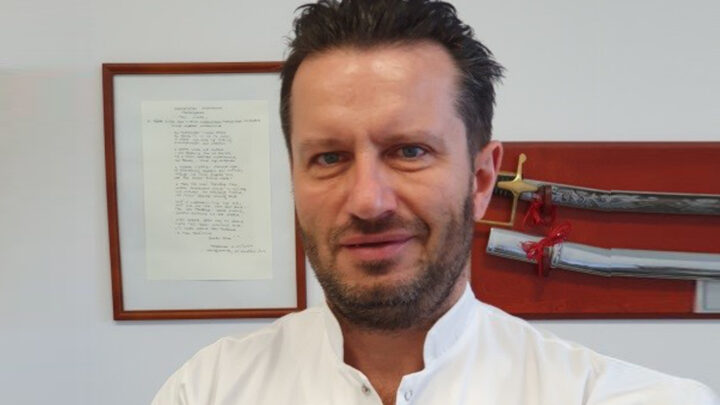
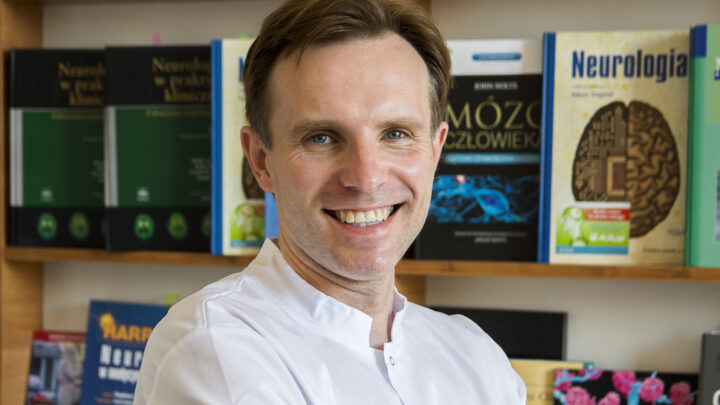
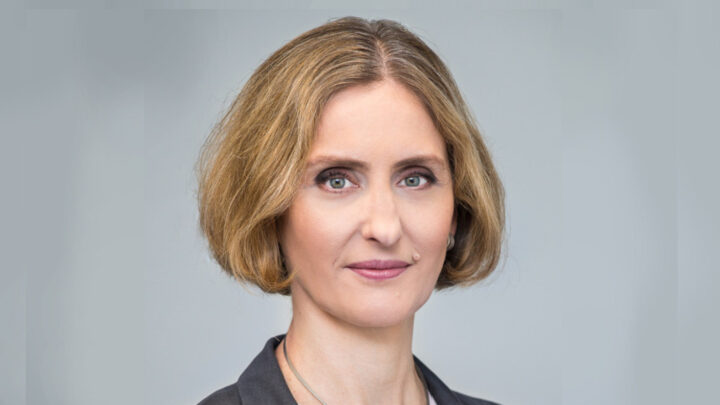
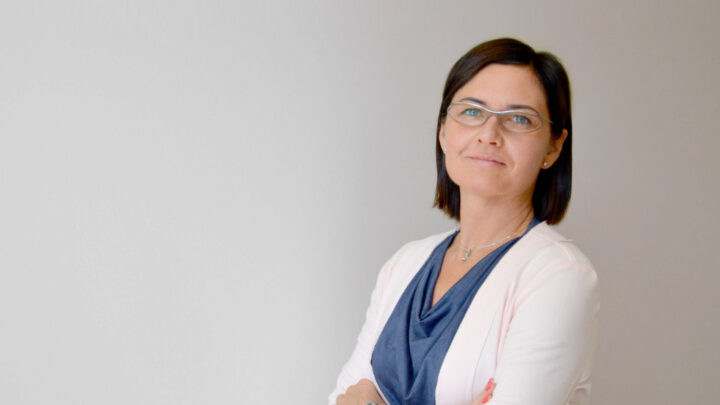
DARIUSZ PATKOWSKI
PIOTR PONIKOWSKI
ANDRZEJ GÓRSKI
KRZYSZTOF NARKIEWICZ
JOLANTA KUJAWA
RAFAŁ PANKOWSKI
PIOTR TRZONKOWSKI
KRZYSZTOF KAŁWAK
HENRYK SKARŻYŃSKI
BARTOSZ KARASZEWSKI
MARTA MIĄCZYŃSKA
IDA FRANIAK PIETRYGA
ORGANIZER



Internationalization enables the exchange of knowledge, experiences and discoveries, allows for multi-faceted use of the research potential of scientists and infrastructure, and contributes to the increase in the quality of teaching. Recognizing the importance of internationalization, the Ministry of Science and Higher Education initiated the establishment of the National Agency for Academic Exchange (NAWA) in October 2017.
NAWA works for the internationalization of Polish science by supporting and stimulating international research cooperation and academic exchange. The agency aims to strengthen scientific excellence, internationalize Polish universities and scientific institutions, as well as to promote Poland – its language and culture in order to build the image of a country offering interesting educational and research opportunities.
These goals are realized thanks to the wide program offer of the Agency:
- Programs for Scientists
- Programs for Institutions
- Student Programs
- Polish language programs

The Minister of Education and Science is the supreme public administration body, which is serviced by the Ministry of Education and Science in the field of government administration departments of education and upbringing as well as higher education and science.
The Ministry of Education and Science was established on January 1, 2021 by the Regulation of the Council of Ministers of December 17, 2020 on the establishment of the Ministry of Education and Science and the abolition of the Ministry of National Education and the Ministry of Science and Higher Education (Journal of Laws, item 2334).
OUR PARTNERS
The Conference of Rectors of Academic Schools in Poland
The Conference of Rectors of Academic Medical Universities
The Polish Academy of Sciences
Copernicus Science Centre
Medical Research Agency
The Łukasiewicz Research Network
FIND US
ul. Polna 40
00-635 Warsaw
Phone : +48 22 390 35 00
Email : biuro@nawa.gov.pl
16-23 Feb 2022
Expo 2020 Dubai